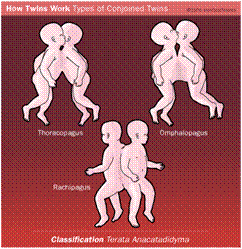
Types of Conjoined Twins
Incomplete separation of fetuses; such fetuses are monochromic and monoamniotic with an incidence of 1 in 52000 births.
· Thoracopagus — joined at thorax 70% (a)
· Omphalopagus — anterior abdominal wall (b)
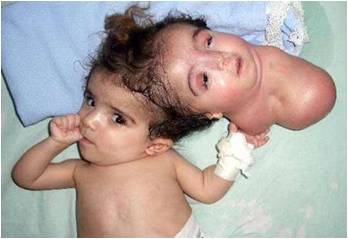
· Craniopagus — skull (c)
· Pyopagus — buttocks and sacrum(d)
· Ischiopagus — ischium (e)
· Diprosopus — two faces. (f)
a-b
c
 d
d
 e
e  f
f
Ultrasound diagnosis
· Separate fetuses with a constant point of connection.
· Absent dividing membranes.
· Umbilical arteries may have differing Doppler wave form.
· Associated anomalies, particularly in diprosopus.
Back to Fetal Wellbeing and Growth