Fetal microphthalmos
· Phenylketonuria - Autosomal recessive condition associated with IUGR, MOPH; prenatal diagnoses can be achieved by amniocentesis and analysis of DNA isolated from amniotic cell culture.
· Pena-shokier syndrome- (Cerebro-oculofacioskeletal syndrome) Sonographically may reveal PH, placentomegaly, hydrops fetalis, joint contractures/ arthrogryposis, micrognathia, small narrow thoracic cavity, hypotelorism and MOPH.
· Amniotic head syndrome- This is a non-inherited condition in which the amniotic bands cause slash defects. Anomalies of the face include asymmetrical clefts,
anencephaly, microcephaly, encephalocele, microphthalmos and transient OH.
· Fanconi's anemia- Autosomal recessive; associated with limb anomalies, absent, hypoplastic or supernumary thumbs, hypoplastic/absent radii, syndactyly, MOPH, microcephaly, renal aplasia, horse shoe kidneys and hydronephrosis. Prenatal diagnosis may be confirmed by increase in chromosomal breakage in amniotic cells when exposed to diepoxybutane.
· Fetal toxoplasmosis- Associated anomalies include microcephaly, MOPH, hydrops, JUGR, hydranencephaly, hydrocephalus secondary to aqueduct stenosis, porencephalic cyst and periventricular calcification. Repatic and spleen calcification has been reported in the newborn.
· Fetal rubella syndrome- Associated anomalies reported include craniostenosis, aqueduct stenosis, cysts of the subependvmal germinal matrix, congenital cataract, MOPH, CHD, esophageal atresia, IUGR.
· Fetal herpes simplex infection- Features include microcephalv. MOPH and IUGR. Cerebral, periventricular, liver and adrenal calcification have been reported in the neonate.
· Fetal alcohol syndrome- This occurs in the fetuses of chronic alcoholic mothers. Associated features include MOPH, microcephaly, micrognathia, cleft lip/palate, CHD, hemangiomas, congenital tumors, diaphragmatic hernia and hydronephrosis.
· Fetal isotretinoin syndrome- Isotretinoin is a teratogenic drug, reported to have caused holoprosencephaly, hydrocephalus, agenesis of the vermis, hypertelorism, MOPH, micrognathia, external ear anomalies and CHD.
· Hydrolethalus syndrome- (Salonen—Herva—Norio syndrome) Is an autosomal recessive condition associated with MOPH, micrognathia, deformed ears, cleft lip/palate, postaxial polydactyly in hands, preaxial polydactyl in feet, omphalocele, CHD, PH, hydrocephalus, DWS, hypoplasia of tibias and bilateral pulmonary agenesis.
· Roberts' syndrome- Inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, the syndrome is associated with IUGR, MOPH, hypertelorism, cataracts, frontal encephalocele, hydrocephalus, facial hemangioma, nuchal cystic hygroma, limb reduction anomaly, clindactyly, clubfeet, renal anomalies and CHD.
· Meckel-Gruber syndrome- This is an autosomal recessive condition associated with occipital encephalocele, hydrocephalus, small BPD, MOPH, CHD, short limbs and cystic dysplasia, giving rise to large kidneys, absent bladder.
· Treacher Collins syndrome- This is an autosomal dominant condition associated with hypoagenesis/agenesis of the mandible, vertebral anomalies, MOPH, micrognathia, cleft palate, CHD and limb anomalies.
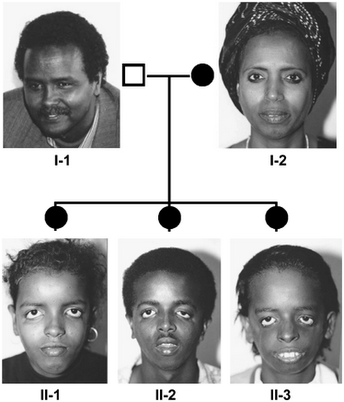
 Treacher Collins syndrome
Treacher Collins syndrome
· Median cleft face syndrome- (Fibronasal dysplasia) Most of these cases are autosomal recessive or dominant. The features associated include a median cleft of the nose and frontal bone, MOPH, hypertelorism, holoprosencephaly, hydrocephalus, choanal atresia, deformed anterior horns of the lateral ventricles, ACC, congenital cataracts, cleft lip/palate, meningocele, encephalocele, clindactyly, camptodactyly and CHD.
· Warfarin embyopathy- Due to maternal warfarin ingestion; the syndrome is associated with hypertelorism, MOPH, large tongue, hydrocephalus, occipital meningocele, CHD, asplenia and limb reduction anomalies.
· Thalidomide embryopathy- Related to maternal ingestion of thalidomide early in pregnancy. The syndrome is unlikely to be seen in utero at the present time as the drug is no longer prescribed in pregnancy. The syndrome is associated with limb anomalies, MOPH, ear abnormalities, renal and intestinal malformation and CHD.
· Glotz's syndrome- X-linked dominant condition associated with MOPH, unilateral anophthalmia, single umbilical artery, syndactyly, polydactyly, adactyly, microcephaly, renal anomalies and foot deformities.
· Goldenhar's syndrome- This is a sporadic condition with rare familial cases. Features include anophthalmia, MOPH, ventricular anomalies, intracranial lipoma/dermoid, anencephaly, hydronephrosis, pulmonary agenesis and cleft palate.
· Holoproscencephaly- (1) Alobar type. This is the most severe, with a monoventricle, fused thalami, absence of falx and corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is horse shoe shaped and lies anteriorly. The dorsal cyst has no overlying brain cortex.
(2) Semilobar type. There is a monoventricle with a rudimentary occipital horn which communicates with a dorsal sac. The thalami are partially fused. (3) Lobar type. The lateral ventricles are fused anteriorly but separated into the occipital horns. The lateral horns are enlarged anteriorly and communicate in the midline.
· Hallermann- streiff syndrome - (Oculomandibulofacial syndrome) Associated features include MOPH, congenital cataracts, low set ears, micrognathia, small pinched nose, microstomia, scaphocephaly or brachycephaly (BPD anomalies).
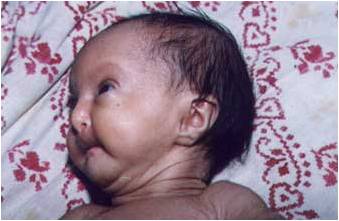
Hallermann- streiff syndrome
· CHARGE syndrome- Autosomal dominant or recessive; associated with MOPH, atresia of choana, PH, CHD, CNS anomalies, ear anomalies, deafness, TOF and VATER association.
· Cohen's syndrome- Probably autosomal recessive; association with MOPH, microcephaly, hypotelorism, micrognathia, prominent ears, syndactyly, thoracic scoliosis, IUGR.
· Aplasia cutis congenita - (Adams—Oliver syndrome) Autosomal recessive, rarely autosomal dominant; features demonstrable on ultrasound include micropthalmia, meningocele, hydrocephalus. TOF, hemangiomas and hands/feet/digit anomalies. The skin and scalp lesions are usually not detectable on sonography.
· Bardet-Biedl syndrome - Autosomal recessive; associated with polydactyly, syndactyly, clindactyly of the 5th finger, urogenital anomalies (hydronephrosis) and CHD.
· Fetal varicella syndrome- Abnormalities reported include IUGR, microcephaly, MOPH, congenital cataract, hypoplasia of limbs, digits, mandible and ribs, equinovarus and calcaneovalgus, hydrocephalus, cerebral hypoplasia, spinal scoliosis, GIT and genitourinary anomalies. Basal ganglia calcification has been reported in the newborn.
· Hypopituitarism- In the fetus and neonate this is likely to be related to familial condition (autosomal recessive or X-linked recessive,) congenital absence of the pituitary gland or secondary to a craniopharyngioma. The fetal sonographic features are likely to present as MOPH, IUGR and postaxial polydactyly. An intracranial mass lesion such as craniopharyngioma may be seen. Congenital hypopituitarism has not yet been reported on antenatal sonography.
· Incontinentia pigmentis (block-Sulzberger syndrome) -This X-linked dominant condition is lethal in males. Associated features include a single umbilical artery, MOPH, microcephaly. hydrocephalus, porencephalic cyst, clubfeet, cataracts, syndactyly and vertebral anomalies.
· Kenny-caffey syndrome- (Tubular stenosis dysplasia) This is an X-ljnked condition; most features of the syndrome become evident postnatally, antenataf diagnosis is therefore likely to be difficult but with a positive family history features like IUGR, MOPH and macrocephaly may point to an affected fetus.
· Lenz's microphthalmos syndrome- The features of this recessive X-linked condition include anophthalmos, MOPH, microcephaly, cleft lip/palate, webbed neck, deformed ears, renal anomalies. CHD and anomalies of finger and toes.
· Neu-Laxova syndrome- This is an autosomal recessive condition associated with IUGR, hypoechoic skeleton, kyphosis, microcephaly, receding forehead, protuberant eyes, MOPH, absent digits, short hands, ‘sickle-like’ long bones, flexion deformities, rockerbottom feet, syndactyly, micrognathia, deformed ears, PH or OH.
· Oculodentoosseous dysplasia- This is an autosomal dominant condition with a variable expressivity associated with MOPH, clindactyly of the 5th finger, syndactyly and camptodactyly of the 4th and 5th fingers, cleft lip/palate, small orbits, hypotelorism, wide mandible and hypoplasia/absence of phalanges of toes and fingers.
· Osteoporosis Pseudoglioma syndrome- This is an autosomal recessive condition associated with MOPH, cataracts, microcephaly, kyphoscoliosis, CHD (VSD).
· Pallister-Hall syndrome- This syndrome is associated with MOPH, microcephaly, hypothalamic hamartoblastoma, renal agenesis and/or renal dysplasia, imperforate anus, postaxial polydactyly, CHD and IUGR. The syndrome has not yet been diagnosed antenatally.
· Proteus syndrome- The characteristics of the syndrome are asymmetric focal overgrowth, macrocephaly, macrodactyly of the hands and feet, subcutaneous vascular tumor, warty pigmented nevi and lipoid visceral tumors. Prenatal ultrasonic findings include hypertrophy and subcutaneous cysts in an extremity, macrodactyly, MOPH, cataracts and intra-abdominal masses (lipomas and lymphangiomas.)
· pseudohypoparathyroidism - This is normally an X-linked condition. Most clinical features develop in early childhood/adult life. MOPH is a congenital feature and may conceivably be detected antenatally.
· Scapuloiliac dysostosis- Probably autosomal dominant; only four cases have been reported. Expected sonographic features will include MOPH, hypertelorism, low set ears, micrognathia, cranium bifidum, clindactyly of fingers and simple partial syndactyly.
· Cat's eye syndrome- Associated with partial terasomy for 22q11 in most cases. Facial anomalies include MOPH, ocular hypertelorism, low set ears; anorectal abnormalities may occur including Hirschsprung’s disease and/or atresia.